- Gold rises over 1% as the US Dollar Index drops below the 98.00 mark.
- Risk appetite lifts Gold as US Dollar and Treasury yields tumble on trade uncertainty.
- EU prepares retaliation plan as August 1 tariff deadline approaches.
- WSJ reports Trump advised not to fire Powell, adding pressure on Fed credibility.
Gold price rallied over 1% on Monday as the US Dollar and US Treasury yields tumbled sharply amid uncertainty over trade deals, amid an overall risk-on mood on the markets. At the time of writing, the XAU/USD trades at $3,397 after bouncing off daily lows of $3,338.
Risk appetite improved as traders await the release of earnings in the United States (US). In the meantime, the August 1 tariff deadline imposed by the White House looms, keeping investors uneasy about trade deals between the US and its three major trading partners, including the European Union (EU), Canada and Mexico.
Trade news revealed that the EU envoys are set to meet as early as this week to formalize a retaliation plan in the event of a possible no-deal scenario with US President Trump, according to Bloomberg.
The Wall Street Journal reported that US Treasury Secretary Bessent recommended Trump not to fire Fed Chair Jerome Powell, as it would cast doubts on the Federal Reserve’s (Fed) independence. This would spark a reaction in the markets, pushing the US Dollar down and US Treasury yields up.
Other news revealed that the People’s Bank of China kept its key lending rates unchanged at its latest meeting, as expected.
This week, the US economic docket remains scarce with the release of housing data, Jobless Claims for the week ending July 19, and Durable Goods Orders data.
Daily digest market movers: Gold rallies as US yields plummet
- US Treasury yields continued to drop as the 10-year Treasury note plunged over six and a half basis points (bps) to 4.356% at the time of writing. Consequently, US real yields, which are calculated by subtracting inflation expectations from the nominal interest rate, are also down six basis points at 1.946%.
- The US Dollar Index (DXY), which tracks the buck’s performance against a basket of six currencies, is down 0.64% at 97.83.
- The EU continues to work on securing a trading agreement, while also having a retaliatory backup draft aimed at targeting €72 billion worth of US exports, which would cover products such as cars, aircraft, bourbon whiskey, digital services, and other key sectors.
- Last week, US economic data remained mixed despite an improvement in Consumer Sentiment, as consumer inflation rose sharply in June, edging toward the 3% threshold. The Producer Price Index (PPI) showed signs of improvement, but a strong Retail Sales report indicates American consumers’ resilience, although prices continued to climb.
- Interest rate probability indicates that the Federal Reserve will maintain its current rates, with odds standing at 97% for a hold and 3% for a 25-basis-point rate cut at the July 30 meeting.
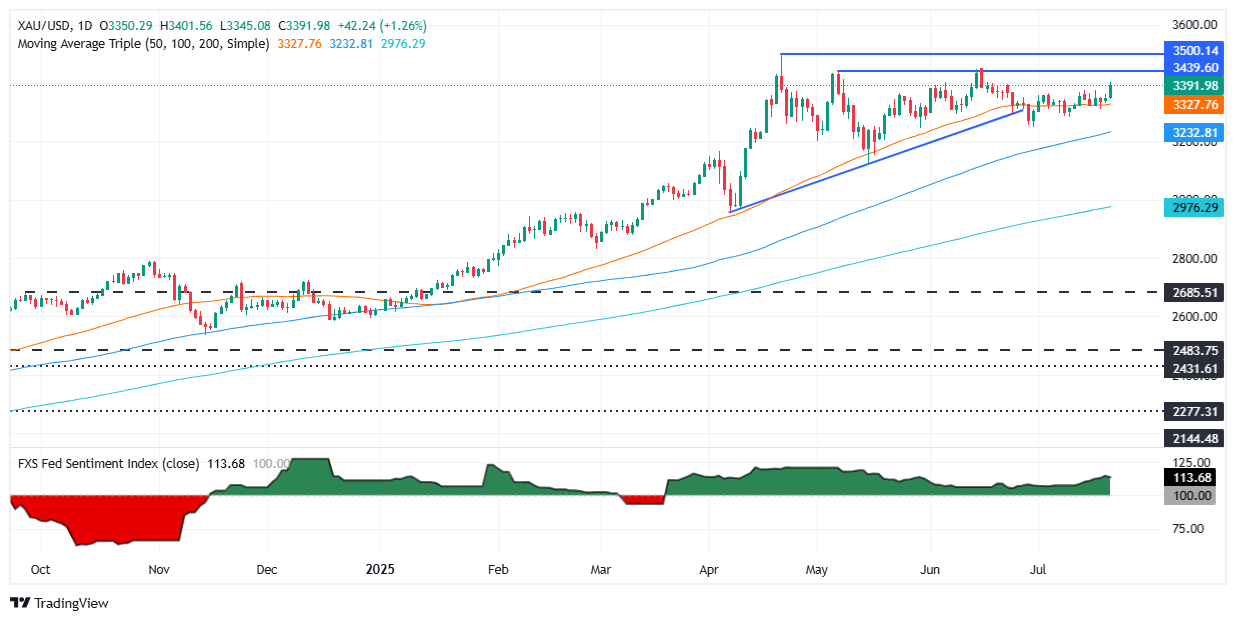
XAU/USD technical outlook: Gold price hits $3,400 after five weeks of trading sideways
Finally, Gold has cleared the top of the $3,300-$3,350 range, reaching a five-week high of $3,401, before settling below the latter, as bullish momentum grows. The Relative Strength Index (RSI) confirms this, as the RSI edges higher toward the 60.00 level, indicating that bulls are in charge.
If XAU/USD ends the day above $3,400, expect a test of the June 16 high of $3,452, ahead of the record high of $3,500. Otherwise, if Gold stays below $3,400, the first support would be $3,350, followed by $3,300. Once cleared, prices could decline to the June 30 low of $3,246, followed by the 100-day Simple Moving Average (SMA) at $3,218.
Fed FAQs
Monetary policy in the US is shaped by the Federal Reserve (Fed). The Fed has two mandates: to achieve price stability and foster full employment. Its primary tool to achieve these goals is by adjusting interest rates.
When prices are rising too quickly and inflation is above the Fed’s 2% target, it raises interest rates, increasing borrowing costs throughout the economy. This results in a stronger US Dollar (USD) as it makes the US a more attractive place for international investors to park their money.
When inflation falls below 2% or the Unemployment Rate is too high, the Fed may lower interest rates to encourage borrowing, which weighs on the Greenback.
The Federal Reserve (Fed) holds eight policy meetings a year, where the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) assesses economic conditions and makes monetary policy decisions.
The FOMC is attended by twelve Fed officials – the seven members of the Board of Governors, the president of the Federal Reserve Bank of New York, and four of the remaining eleven regional Reserve Bank presidents, who serve one-year terms on a rotating basis.
In extreme situations, the Federal Reserve may resort to a policy named Quantitative Easing (QE). QE is the process by which the Fed substantially increases the flow of credit in a stuck financial system.
It is a non-standard policy measure used during crises or when inflation is extremely low. It was the Fed’s weapon of choice during the Great Financial Crisis in 2008. It involves the Fed printing more Dollars and using them to buy high grade bonds from financial institutions. QE usually weakens the US Dollar.
Quantitative tightening (QT) is the reverse process of QE, whereby the Federal Reserve stops buying bonds from financial institutions and does not reinvest the principal from the bonds it holds maturing, to purchase new bonds. It is usually positive for the value of the US Dollar.





